- Document History
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report to a Moderator
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report to a Moderator
Biosignal Logger and Player
Biosignals often contain noise. For example, an electrocardiogram (ECG) often contains power line interference. You can use adaptive filters to separate the signal you need from the original, noisy biosignal.
The Biosignal Logger and Player offers a function using adaptive filters to reduce the noise in a noisy biosignal. This application includes the following features:
- Acquiring biosignal data from National Instruments hardware, such as NI DAQ and NI ELVIS II.
- Configuring channel settings for extracting signals from noisy biosignals.
- Supporting the least mean squares (LMS) and normalized least mean squares (NLMS) algorithms. You can apply these algorithms to the adaptive filter to extract real-time biosignals.
- Logging data to a binary measurement file (.tdms).
Setting Up the Biosignal Logger and Player Hardware Components
As a noise reduction application using adaptive filter method, the Biosignal Logger and Player requires signals from two channels. One channel contains the original, noisy signals. The second channel contains the noise signal, which is considered a reference. The Biosignal Logger and Player requires you to set up hardware. Setting up the hardware depends on the application you need to reduce noise.
Setting Up a Power Line Cancellation Application
If you use a twelve-lead or three-lead ECG instrument to measure an ECG, you can use any of the leads as the original signal. For the reference signal, use the common-mode signal, which usually is recorded at the right leg reference electrode or other reference electrode. Refer to the article [1] for more information about lead and reference electrodes. For example, you can use NI ELVIS II and a third-party ECG sensor device, such as the Vernier (http://www.vernier.com) EKG Sensor, to configure a power line cancellation system.
If you use the NI ELVIS II and Vernier EKG Sensor, connect the EKG Sensor to the input of the Vernier Analog Proto Board Connector. Connect the output of the Vernier Analog Proto Board Connector to one of the NI ELVIS II AI ports. This connection obtains the original noisy biosignal.
To obtain the reference signal by using NI ELVIS II and the Vernier EKG Sensor, you can complete one of the following configurations.
- (Recommended) Connect a second Vernier EKG Sensor to a second Vernier Analog Proto Board Connector. Do not connect this EKG Sensor to the human body. Connect the output of the Vernier Analog Proto Board Connector to another AI port on the NI ELVIS II. This connection obtains the reference signal.
- Connect the AI port with a wire. Place the opposite end of this wire near the power source. This AI channel obtains the reference signal. The following figure shows the hardware components of a power line cancellation application by using this configuration.
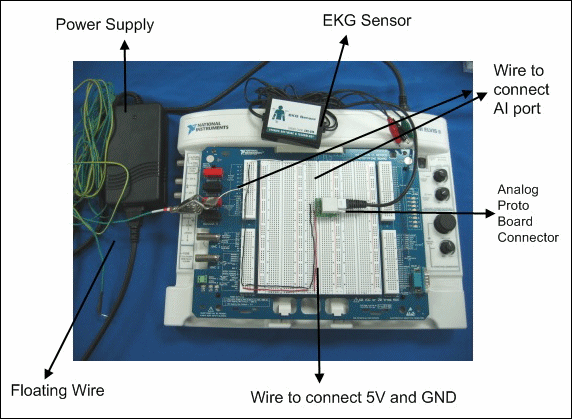
After setting up the hardware components of the application, launch the Online Biosignal Noise Reduction Data Logger to configure the software components to reduce noise.
Setting Up a Fetal ECG Extraction Application
A fetal electrocardiogram (FECG), which you measure from the maternal abdomen, often contains a strong maternal electrocardiogram (ECG). You can use the Online Biosignal Noise Reduction Data Logger to extract the FECG from a noisy biosignal.
Typically, a twelve-lead ECG instrument has six chest leads and six limb leads. This applications utilizes the six chest leads in two groups. One group of leads obtains the signals for the original signal. These leads are placed on the abdomen, according to the following figure.
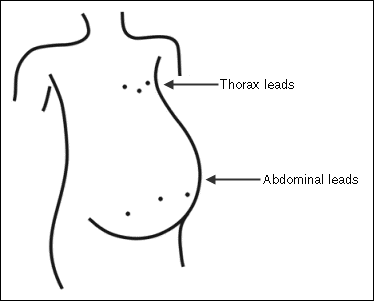
When choosing the exact locations of these leads, choose locations on the maternal abdomen such that a good FECG signal-to-noise ratio is obtained. That is, as if no maternal ECG is present. Refer to the book [2] for more information about lead placement for FECG extraction. The second group of leads obtains the signals for the reference signal. These leads are placed on the chest, near the thorax, according to the previous figure.
After placing the leads, verify that each lead corresponds to an AI port number on the hardware instrument, such as NI DAQ or NI ELVIS II. In the Biosignal Logger, you must set one of the thorax leads as the reference signal and one of the abdominal leads as the original signal.
After setting up the hardware components of the application, launch the Biosignal Logger to configure the software components to reduce noise.
Reducing Noise
Complete the following steps to reduce the noise in a noisy biosignal.
1. Launch the Biosignal Logger and Player.
2. Click the Logger Settings button to display the Configure dialog box.
a) AI Channel step. This step is to set the physical channels.
i. Choose a device from the device list.
ii. In Physical channel control, select two channels you want to use for the noisy ECG and noise reference.
iii. Click add button to add these two channels.
iv. Press Next to go to the Virtual Channel Settings step.
b) Virtual Channel Settings. This step is to set virtual calculation channel.
i. Set channel name and unit name for the calculated channel.
ii. Select Adaptive Filter method from the Type ring.
iii. Select the channel you want to use for the noisy ECG and noise reference by using the Channel for signal and Channel for reference pull-down menus, respectively.
iv. Set the adaptive filter parameters, such as the type, step size, and filter order.
v. Press Next to go to the Logging setting step.
c) Logging settings. This step is to set logging parameters.
i. In the View Sequence part, you could change the view order of all the physical and virtual channels.
ii. Click Log button to log or unlog a channel into tdms file.
iii. You could set some general info of this logging process like Operator name, Note and TDMS path.
iv. You could select a stop criterion to terminate the logging process automatically after some time duration or the file size is larger than some threshold.
3. Click the OK button to close the Configure dialog box.
4. Click the Start button to start acquiring data and to apply adaptive filtering while extracting the biosignal.
5. (Optional) Click the Log button to start logging the data to a .tdms file.
6. Click the Stop button to stop acquiring data. If you clicked the Log button while the application ran, the data saves to the file path you specified as a .tdms file.
Note You can use the to convert the log file this application saves from a .tdms file type to another file type. |
References:
[1] Thakor, N.V.; Zhu, Y.-S. 1991. "Applications of adaptive filtering to ECG analysis: noise cancellation and arrhythmia detection." IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, vol. 38: 785-794
[2] Callaerts, D.; J. Vandewalle; W. Sansen; J. Janssens; and G. Vantrappen. 1994. Acquisition and processing of the antepartum FECG. In A Critical Appraisal of Fetal Surveillance, edited by H.P. van Deijn and F.J.A. Copray. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier Science B.V.
