- Document History
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report to a Moderator
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report to a Moderator
Contact Information
University: Univesity of Maryland Eastern Shore
Team Member(s): Xavier Henry, Mohamad Dyab, Moustapha Diab, Dinbanimibofa Ari,
Faculty Advisors: Abhijit Nagchaudhuri & Madhumi Mitra
Email Address: xhenry@umes.edu
Country: USA
Project Information
Title:
Experimental prototype of a semi autonomous platform to monitor water quality in sensitive aquatic ecosystems, USA
Description:
Eutrophication (nutrient-enrichment) and subsequent harmful algal blooms (HAB's) pose serious threats to many sensitive aquatic ecosystems around the Delmarva Peninsula. Changes in pH, salinity, dissolved oxygen, and turbidity can adversely impact trophic structures, so monitoring these parameters, especially via ROV’s, is crucial for determining ecosystem vigor. This provided the motivation to develop a low cost, multisensory, semi-autonomous platform for recording water quality data from coastal water bodies of the Delmarva Peninsula.
Products:
LabVIEW system design software & Lego Mindstorms NXT
The Challenge:
Eutrophication (nutrient-enrichment) and harmful algal blooms (HAB's) pose serious threats to the many of our coastal water bodies. As a consequence of increased primary productivity, changes in pH, salinity, dissolved oxygen, and turbidity could impact various marine and estuarine ecosystems in an adverse manner. Furthermore, the ability to frequently access such regions with minimal footprint often poses significant challenges to in-situ monitoring efforts. These conditions provided the motivation to develop a cost-effective, multisensory, semi-autonomous platform for applications in recording the water quality data from the coastal water bodies of the Delmarva Peninsula.
The Solution:
LabVIEW, Lego Mindstorm’s NXT, and several water quality Vernier sensors were used in combination with a dual control (RC or autonomous) airboat and Geographical Positioning System (GPS) for this purpose in a Fall 2010 experiential learning and research project for undergraduate and graduate students in engineering and resource sciences. Preliminary tests were done with the platform, dubbed AQUABOT for recording water quality data from the Assateague, Chesapeake (Maryland), and Chincoteague (Virginia) Bays of the Delmarva Peninsula in areas where communities, such as seagrass meadows, are impacted by increased eutrophic conditions. In addition, the pH, salinity, and dissolved oxygen data trends from the AQUABOT were compared to the multi-parameter YSI environmental monitoring unit, and subsequent sensory data was mapped using the ArcGIS geospatial information systems software. The faculty members in the department of Natural Sciences and Engineering programs at the University of Maryland Eastern Shore (UMES) collaborated to initiate this effort. They have integrated project assignments related to enhancement, data collection, and data analysis utilizing the multi-sensor platform in Marine Botany and Instrumentation courses offered in the fall to undergraduate students in the environmental sciences and engineering majors respectively. Efforts to improve the platform and increase instrumentation capabilities are currently underway.
The use of LabVIEW and Lego Mindstorm’s NXT provided a low-cost yet powerful, intuitive, and fun solution to attacking a major engineering and environmental challenge whose implications can have profound effects on communities in the Delmarva region and much farther afield.

Figure 1. Initial test configurations with NXT- Vernier sensor systems.
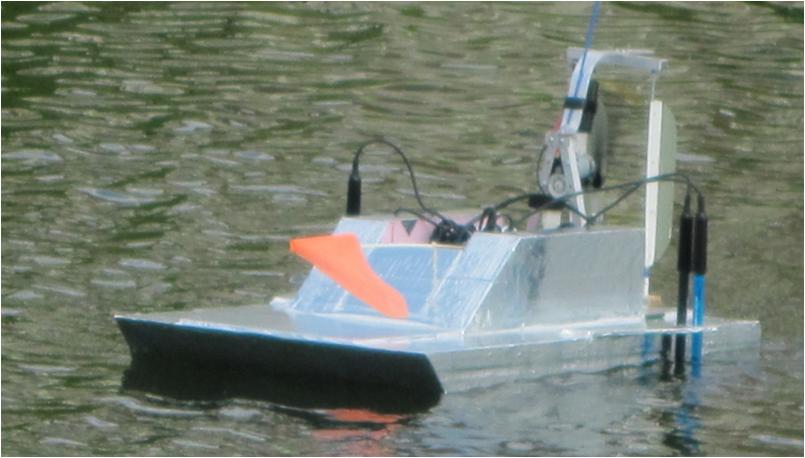

Figure 2. AQUABOT platform in operation at Racoon Point, Maryland.
Figure 3. Students in Marine Botany (BIOL 203) readying the AQUABOT for mission at Assateague Bay, Maryland.

Figure 4. Students in Marine Botany (BIOL 203) retrieving the AQUABOT after a mission at Chincoteague Bay, Virginia.
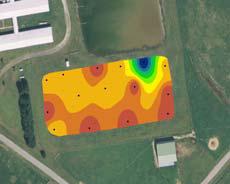
Figure 5. Surface interpolation of pH data retrieved from a pond in the UMES campus by Engineering Instrumentation students (ENGE 380).
