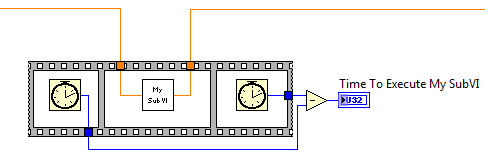
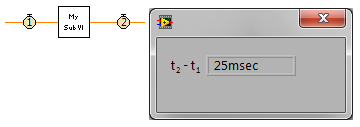
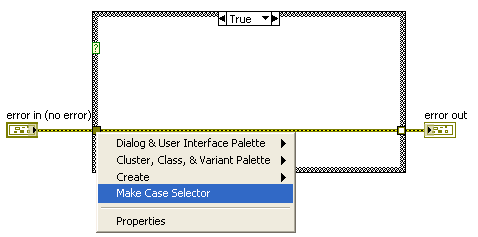
Community Browser
-
NI Community
- Welcome & Announcements
-
Discussion Forums
- Most Active Software Boards
- Most Active Hardware Boards
-
Additional NI Product Boards
- Academic Hardware Products (myDAQ, myRIO)
- Automotive and Embedded Networks
- DAQExpress
- DASYLab
- Digital Multimeters (DMMs) and Precision DC Sources
- Driver Development Kit (DDK)
- Dynamic Signal Acquisition
- FOUNDATION Fieldbus
- High-Speed Digitizers
- Industrial Communications
- IF-RIO
- LabVIEW Communications System Design Suite
- LabVIEW Electrical Power Toolkit
- LabVIEW Embedded
- LabVIEW for LEGO MINDSTORMS and LabVIEW for Education
- LabVIEW MathScript RT Module
- LabVIEW Web UI Builder and Data Dashboard
- MATRIXx
- Hobbyist Toolkit
- Measure
- NI Package Manager (NIPM)
- Phase Matrix Products
- RF Measurement Devices
- SignalExpress
- Signal Generators
- Switch Hardware and Software
- USRP Software Radio
- NI ELVIS
- VeriStand
- NI VideoMASTER and NI AudioMASTER
- VirtualBench
- Volume License Manager and Automated Software Installation
- VXI and VME
- Wireless Sensor Networks
- PAtools
- Special Interest Boards
- Community Documents
- Example Programs
-
User Groups
-
Local User Groups (LUGs)
- Denver - ALARM
- Bay Area LabVIEW User Group
- British Columbia LabVIEW User Group Community
- Chicago LabVIEW User Group
- Egypt NI Chapter
- GUNS
- Houston Area LabVIEW Community
- LabVIEW - University of Applied Sciences Esslingen
- [IDLE] LabVIEW User Group Stuttgart
- LUGG - LabVIEW User Group at Goddard
- LUGNuts: LabVIEW User Group for Connecticut
- Madison LabVIEW User Group Community
- Mass Compilers
- Melbourne LabVIEW User Group
- Midlands LabVIEW User Group
- Milwaukee LabVIEW Community
- Minneapolis LabVIEW User Group
- CSLUG - Central South LabVIEW User Group (UK)
- Nebraska LabVIEW User Community
- New Zealand LabVIEW Users Group
- NI UK and Ireland LabVIEW User Group
- NOCLUG
- Orange County LabVIEW Community
- Ottawa and Montréal LabVIEW User Community
- Washington Community Group
- Phoenix LabVIEW User Group (PLUG)
- Politechnika Warszawska
- PolŚl
- Rutherford Appleton Laboratory
- Sacramento Area LabVIEW User Group
- San Diego LabVIEW Users
- Sheffield LabVIEW User Group
- South East Michigan LabVIEW User Group
- Stockholm LabVIEW User Group (STHLUG)
- Southern Ontario LabVIEW User Group Community
- SoWLUG (UK)
- Space Coast Area LabVIEW User Group
- Sydney User Group
- Top of Utah LabVIEW User Group
- Utahns Using TestStand (UUT)
- UVLabVIEW
- Western NY LabVIEW User Group
- Western PA LabVIEW Users
- Orlando LabVIEW User Group
- Aberdeen LabVIEW User Group (Maryland)
- Gainesville LabVIEW User Group
- LabVIEW Team Indonesia
- Ireland LabVIEW User Group Community
- Louisville KY LabView User Group
- NWUKLUG
- LVUG Hamburg
- LabVIEW User Group Munich
- LUGE - Rhône-Alpes et plus loin
- London LabVIEW User Group
- VeriStand: Romania Team
- DutLUG - Dutch LabVIEW Usergroup
- WaFL - Salt Lake City Utah USA
- Highland Rim LabVIEW User Group
- NOBLUG - North Of Britain LabVIEW User Group
- North Oakland County LabVIEW User Group
- Oregon LabVIEW User Group
- WUELUG - Würzburg LabVIEW User Group (DE)
- LabVIEW User Group Euregio
- Silesian LabVIEW User Group (PL)
- Indian LabVIEW Users Group (IndLUG)
- West Sweden LabVIEW User Group
- Advanced LabVIEW User Group Denmark
- Automated T&M User Group Denmark
- UKTAG – UK Test Automation Group
- Budapest LabVIEW User Group (BudLUG)
- South Sweden LabVIEW User Group
- GLA Summit - For all LabVIEW and TestStand Enthusiasts!
- Bangalore LUG (BlrLUG)
- Chennai LUG (CHNLUG)
- Hyderabad LUG (HydLUG)
- LUG of Kolkata & East India (EastLUG)
- Delhi NCR (NCRLUG)
- Montreal/Quebec LabVIEW User Group Community - QLUG
- Zero Mile LUG of Nagpur (ZMLUG)
- LabVIEW LATAM
- LabVIEW User Group Berlin
- WPAFB NI User Group
- Rhein-Main Local User Group (RMLUG)
- Huntsville Alabama LabVIEW User Group
- LabVIEW Vietnam
- [IDLE] ALVIN
- [IDLE] Barcelona LabVIEW Academic User Group
- [IDLE] The Boston LabVIEW User Group Community
- [IDLE] Brazil User Group
- [IDLE] Calgary LabVIEW User Group Community
- [IDLE] CLUG : Cambridge LabVIEW User Group (UK)
- [IDLE] CLUG - Charlotte LabVIEW User Group
- [IDLE] Central Texas LabVIEW User Community
- [IDLE] Cowtown G Slingers - Fort Worth LabVIEW User Group
- [IDLE] Dallas User Group Community
- [IDLE] Grupo de Usuarios LabVIEW - Chile
- [IDLE] Indianapolis User Group
- [IDLE] Israel LabVIEW User Group
- [IDLE] LA LabVIEW User Group
- [IDLE] LabVIEW User Group Kaernten
- [IDLE] LabVIEW User Group Steiermark
- [IDLE] தமிழினி
- Academic & University Groups
-
Special Interest Groups
- Actor Framework
- Biomedical User Group
- Certified LabVIEW Architects (CLAs)
- DIY LabVIEW Crew
- LabVIEW APIs
- LabVIEW Champions
- LabVIEW Development Best Practices
- LabVIEW Web Development
- NI Labs
- NI Linux Real-Time
- NI Tools Network Developer Center
- UI Interest Group
- VI Analyzer Enthusiasts
- [Archive] Multisim Custom Simulation Analyses and Instruments
- [Archive] NI Circuit Design Community
- [Archive] NI VeriStand Add-Ons
- [Archive] Reference Design Portal
- [Archive] Volume License Agreement Community
- 3D Vision
- Continuous Integration
- G#
- GDS(Goop Development Suite)
- GPU Computing
- Hardware Developers Community - NI sbRIO & SOM
- JKI State Machine Objects
- LabVIEW Architects Forum
- LabVIEW Channel Wires
- LabVIEW Cloud Toolkits
- Linux Users
- Unit Testing Group
- Distributed Control & Automation Framework (DCAF)
- User Group Resource Center
- User Group Advisory Council
- LabVIEW FPGA Developer Center
- AR Drone Toolkit for LabVIEW - LVH
- Driver Development Kit (DDK) Programmers
- Hidden Gems in vi.lib
- myRIO Balancing Robot
- ROS for LabVIEW(TM) Software
- LabVIEW Project Providers
- Power Electronics Development Center
- LabVIEW Digest Programming Challenges
- Python and NI
- LabVIEW Automotive Ethernet
- NI Web Technology Lead User Group
- QControl Enthusiasts
- Lab Software
- User Group Lead Network
- CMC Driver Framework
- JDP Science Tools
- LabVIEW in Finance
- Nonlinear Fitting
- Git User Group
- Test System Security
- Product Groups
-
Partner Groups
- DQMH Consortium Toolkits
- DATA AHEAD toolkit support
- GCentral
- SAPHIR - Toolkits
- Advanced Plotting Toolkit
- Sound and Vibration
- Next Steps - LabVIEW RIO Evaluation Kit
- Neosoft Technologies
- Coherent Solutions Optical Modules
- BLT for LabVIEW (Build, License, Track)
- Test Systems Strategies Inc (TSSI)
- NSWC Crane LabVIEW User Group
- NAVSEA Test & Measurement User Group
-
Local User Groups (LUGs)
-
Idea Exchange
- Data Acquisition Idea Exchange
- DIAdem Idea Exchange
- LabVIEW Idea Exchange
- LabVIEW FPGA Idea Exchange
- LabVIEW Real-Time Idea Exchange
- LabWindows/CVI Idea Exchange
- Multisim and Ultiboard Idea Exchange
- NI Measurement Studio Idea Exchange
- NI Package Management Idea Exchange
- NI TestStand Idea Exchange
- PXI and Instrumentation Idea Exchange
- Vision Idea Exchange
- Additional NI Software Idea Exchange
- Blogs
- Events & Competitions
- Optimal+
- Regional Communities
- NI Partner Hub
View Ideas...
Labels
-
Analysis & Computation
297 -
Development & API
2 -
Development Tools
1 -
Execution & Performance
990 -
Feed management
1 -
HW Connectivity
111 -
Installation & Upgrade
262 -
Networking Communications
180 -
Package creation
1 -
Package distribution
1 -
Third party integration & APIs
273 -
UI & Usability
5,313 -
VeriStand
1
Idea Statuses
- New 2,936
- In Development 0
- In Beta 1
- Declined 2,616
- Duplicate 698
- Completed 323
- Already Implemented 111
- Archived 0
Top Authors
| User | Kudos |
|---|---|
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 |
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Options
- Mark all as New
- Mark all as Read
- Float this item to the top
- Subscribe
- Bookmark
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
Showing ideas with label Execution & Performance.
Show all ideas
Status:
Completed
Submitted by
 vitoi
on
07-16-2012
03:36 AM
78
Comment
vitoi
on
07-16-2012
03:36 AM
78
Comment
Status:
Declined
Submitted by
 JackDunaway
on
06-15-2009
07:00 PM
29
Comment
JackDunaway
on
06-15-2009
07:00 PM
29
Comment
Status:
New
Submitted by
 inversion
on
03-03-2011
04:23 AM
23
Comment
inversion
on
03-03-2011
04:23 AM
23
Comment
Labels:
Status:
Completed
Submitted by
 altenbach
altenbach
 on
06-03-2009
11:19 AM
38
Comment
on
06-03-2009
11:19 AM
38
Comment
Status:
Completed
Submitted by
 NelsonUWP
on
07-31-2009
08:05 AM
21
Comment
NelsonUWP
on
07-31-2009
08:05 AM
21
Comment
Labels:
- Tags:
- Programming_Speedup
Status:
Completed
Submitted by
 JackDunaway
on
06-04-2009
05:38 PM
17
Comment
JackDunaway
on
06-04-2009
05:38 PM
17
Comment
Status:
Declined
Submitted by
 Jim_Kring
Jim_Kring
 on
12-10-2009
08:08 PM
19
Comment
on
12-10-2009
08:08 PM
19
Comment
Status:
Completed
Submitted by
 falkpl
on
06-02-2009
03:12 PM
21
Comment
falkpl
on
06-02-2009
03:12 PM
21
Comment
Labels:
Status:
Duplicate
Submitted by
 ClaudioH
on
03-13-2011
06:48 PM
12
Comment
ClaudioH
on
03-13-2011
06:48 PM
12
Comment
Status:
New
Submitted by
 JackDunaway
on
06-12-2009
09:19 PM
32
Comment
JackDunaway
on
06-12-2009
09:19 PM
32
Comment
Status:
New
Submitted by
 fabric
on
09-09-2012
01:10 AM
18
Comment
fabric
on
09-09-2012
01:10 AM
18
Comment
Labels:
Status:
Completed
Submitted by
 jgcode
on
08-19-2010
02:01 AM
14
Comment
jgcode
on
08-19-2010
02:01 AM
14
Comment
Status:
New
Submitted by
 Broken_Arrow
Broken_Arrow
 on
09-25-2009
11:07 AM
30
Comment
on
09-25-2009
11:07 AM
30
Comment
- Tags:
- BD_View
- documentation
- Good-Idea
Status:
Declined
Submitted by
 JackDunaway
on
11-14-2009
06:12 PM
17
Comment
JackDunaway
on
11-14-2009
06:12 PM
17
Comment
Status:
New
Submitted by
 jlokanis
jlokanis
 on
06-25-2009
04:47 PM
29
Comment
on
06-25-2009
04:47 PM
29
Comment
Status:
New
Submitted by
 Broken_Arrow
Broken_Arrow
 on
10-28-2010
11:42 AM
13
Comment
on
10-28-2010
11:42 AM
13
Comment
- Tags:
- FP view
- front_panel
Status:
New
Submitted by
 Darin.K
on
02-09-2011
01:51 PM
15
Comment
Darin.K
on
02-09-2011
01:51 PM
15
Comment
Status:
New
Submitted by
 ErnieH
on
02-25-2010
08:41 AM
37
Comment
ErnieH
on
02-25-2010
08:41 AM
37
Comment
Labels:
- Tags:
- build
- executable
- RTE
Status:
New
Submitted by
AristosQueue (NI)
on
08-13-2012
10:34 AM
21
Comment
Labels: